BT-13 Central Texas Wing

Description:
Base:
San Marcos, TX
Website:
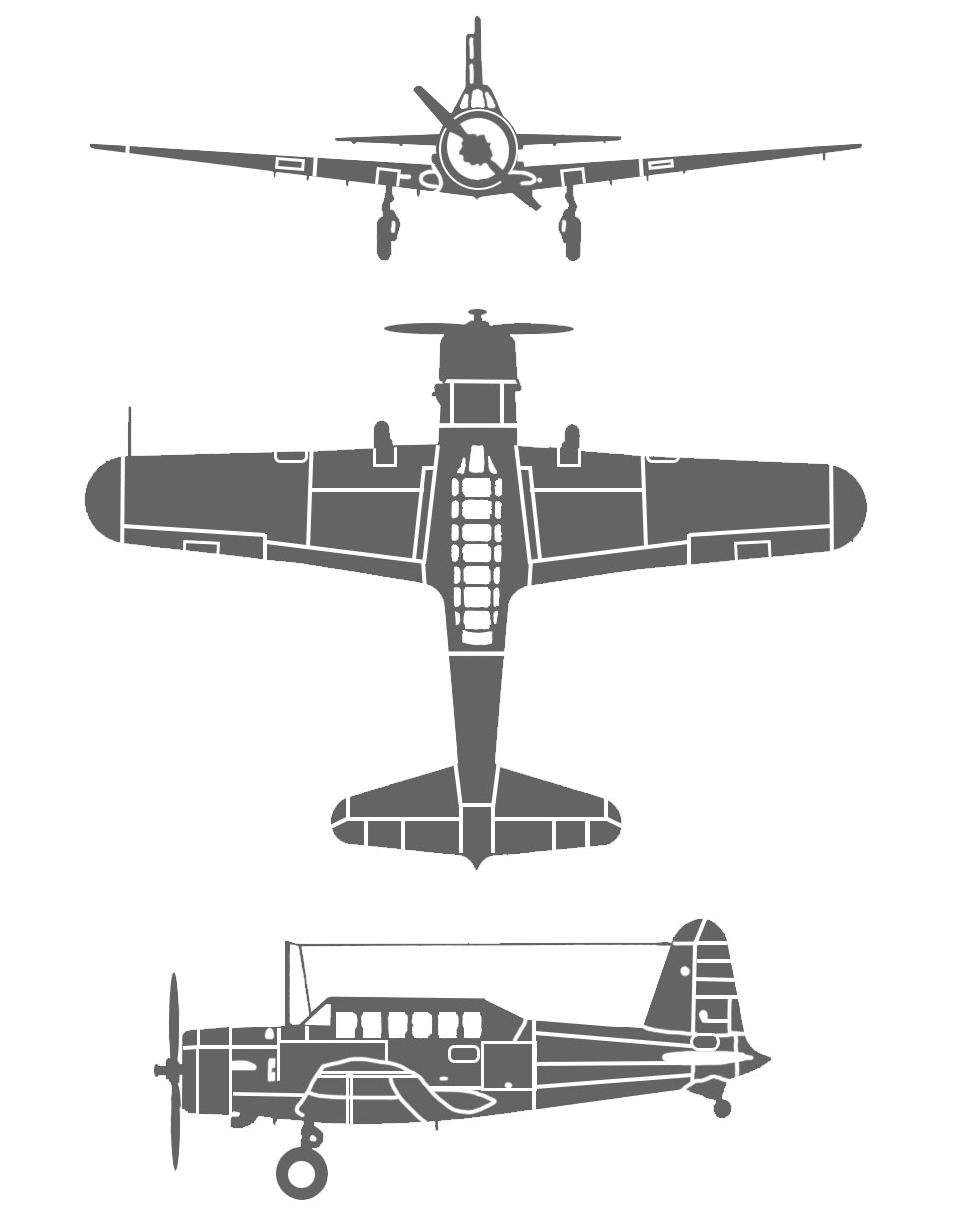
| BT-13 Specs | |
|---|---|
| Role | Trainer |
| Manufacturer | Vultee Aircraft |
| Introduced | Jun 1940 |
| Power | 1 × Pratt & Whitney R-985-AN-1 nine-cylinder air-cooled radial engine, 450 hp |
| Length | 28 ft 10 in |
| Height | 11 ft 6 in |
| Wingspan | 42 ft 0 in |
| Range | 725 mi |
The BT-13 is an American WWII-era Basic Trainer aircraft. It is a fixed-gear, low-wing taildragger with a crew of two sitting in tandem. When production ended in 1944, approximately 11,537 Valiants were built.
It was flown by most American pilots in transitioning from Primary trainers like the PT-19 to more advanced trainers like the AT-6. The BT-13 was more complex than the Primary Trainer and required the use of a two-way radio, landing flaps, and a two-position, and had a controllable-pitch prop.
The BT-13 was nick-named the “Vultee Vibrator” by its pilots for its most remarkable characteristic- a tendency to shake violently as it approached stall speed.
The Vultee BT-13 Valiant was an American basic trainer aircraft from the World War II era, produced by Vultee Aircraft for the U.S. Army Air Corps and later the U.S. Army Air Forces. A later variant of the BT-13 used by the USAAC/USAAF was designated the BT-15 Valiant. In contrast, an identical model used by the U.S. Navy was referred to as the SNV and was utilized to train naval aviators for the U.S. Navy and its sister services, the U.S. Marine Corps and the U.S. Coast Guard.

